 Hello, World
Hello, World
The purpose of this assignment is to introduce you to programming in Java and familiarize you with the mechanics of preparing and submitting assignment solutions.
As part of these instructions, you will write, compile, and execute the program HelloWorld.java.
~/Desktop/hello> javac HelloWorld.java ~/Desktop/hello> java HelloWorld Hello, World
~/Desktop/hello> javac HelloGoodbye.java ~/Desktop/hello> java HelloGoodbye Kevin Bob Hello Kevin and Bob. Goodbye Bob and Kevin. ~/Desktop/hello> java HelloGoodbye Alejandra Bahati Hello Alejandra and Bahati. Goodbye Bahati and Alejandra.
RightTriangle that takes three int
command-line arguments
and determines whether they constitute the side lengths of some right triangle.
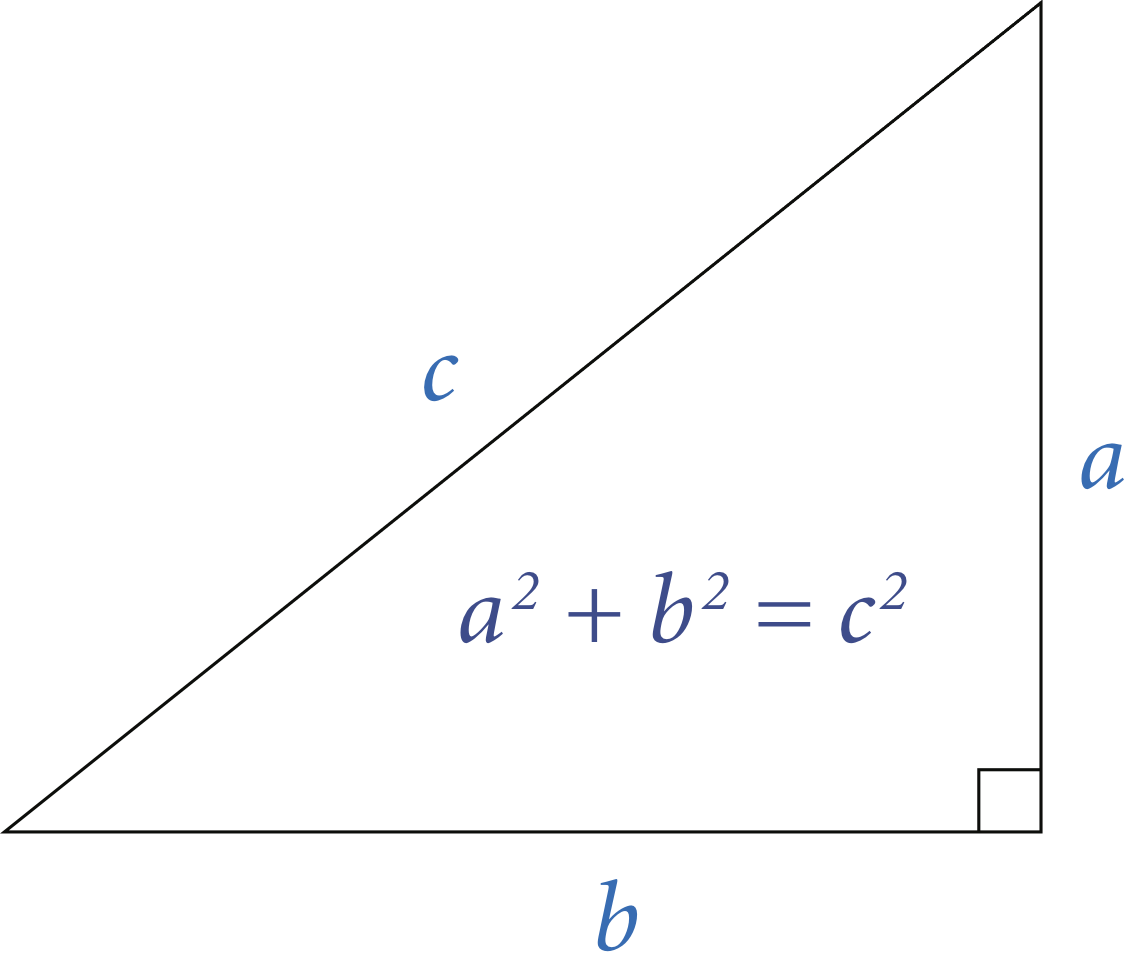
The following two conditions are necessary and sufficient:
~/Desktop/hello> javac RightTriangle.java ~/Desktop/hello> java RightTriangle 3 4 5 true ~/Desktop/hello> java RightTriangle 13 12 5 true ~/Desktop/hello> java RightTriangle 1 2 3 false ~/Desktop/hello> java RightTriangle -3 4 -5 false
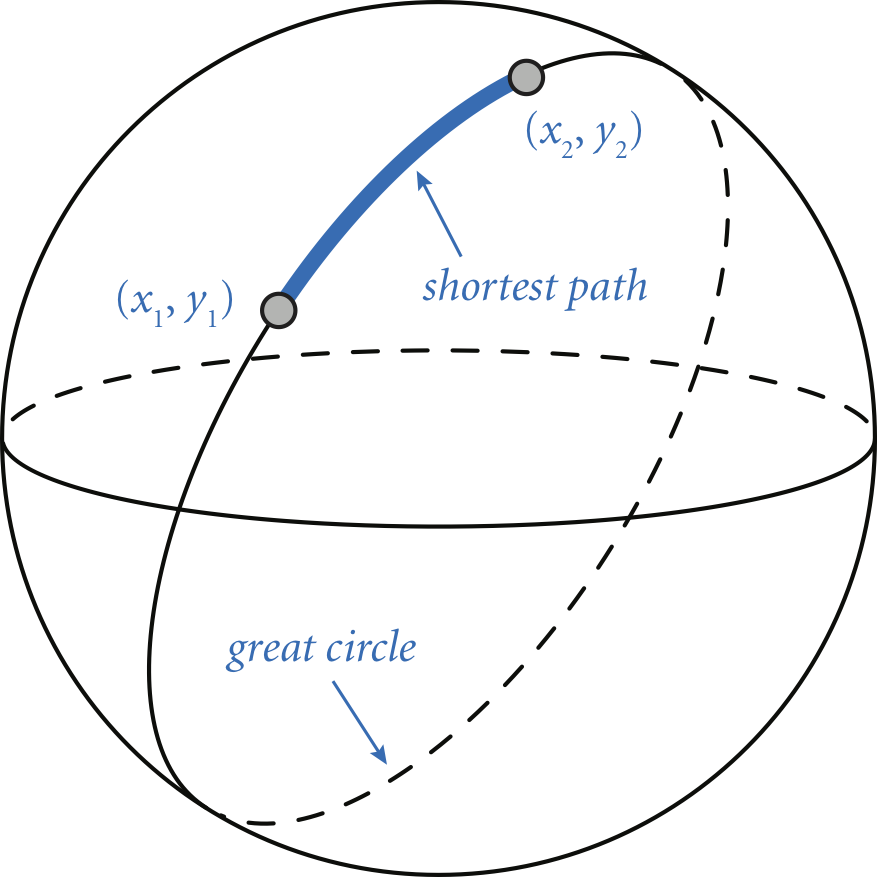
Write a program GreatCircle.java that takes four double command-line
arguments \(x_1\), \(y_1\), \(x_2\), and \(y_2\)—the latitude and longitude (in degrees)
of two points on the surface of the earth—and prints
the great-circle distance (in kilometers) between them.
Use the following
Haversine formula
\[
distance \; = \; 2r \arcsin \left ( \sqrt{ \sin^2 \left ( \frac{x_2 - x_1}{2} \right ) + \cos x_1 \cos x_2 \sin^2 \left ( \frac{y_2 - y_1}{2} \right ) } \right )
\]
where \(r = \text{6,371.0}\) is the mean radius of the Earth (in kilometers).
~/Desktop/hello> javac GreatCircle.java ~/Desktop/hello> java GreatCircle 40.35 74.65 48.87 -2.33 // Princeton to Paris 5902.927099258561 kilometers ~/Desktop/hello> java GreatCircle 60.0 15.0 120.0 105.0 // for debugging 4604.53989281927 kilometers
Hint: The command-line arguments are given in degrees but
Java’s trigonometric functions use radians.
Use Math.toRadians() to convert from degrees to radians.
Although the Earth is not a perfect sphere, this formula is a good approximation to the true distance.
Write a program CMYKtoRGB.java that converts from CMYK format to RGB format
using these mathematical formulas:
\( \begin{align*} white \;&=\; 1 - black \\ red \;&=\; 255 \; \times \; white \; \times \; (1 - cyan) \\ green \;&=\; 255 \; \times \; white \; \times \; (1 - magenta) \\ blue \;&=\; 255 \; \times \; white \; \times \; (1 - yellow) \end{align*} \)Your program must take four
double command-line arguments
cyan, magenta, yellow, and black;
compute the corresponding RGB values, each rounded to the nearest integer;
and print the RGB values, as in the following sample executions:
~/Desktop/hello> javac CMYKtoRGB.java ~/Desktop/hello> java CMYKtoRGB 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 // magenta red = 255 green = 0 blue = 255 ~/Desktop/hello> java CMYKtoRGB 0.0 0.4392156862745098 1.0 0.0 // Princeton orange red = 255 green = 143 blue = 0
Submission.
Submit a .zip file containing
HelloWorld.java,
HelloGoodbye.java,
RightTriangle.java,
GreatCircle.java, and
CMYKtoRGB.java.
You may not call library functions except those in the java.lang
(such as Integer.parseInt() and Math.sqrt()).
Do not use loops, conditional statements, arrays, or other Java features that have not yet been
introduced in the course.